Mood Mapping
Exploring Emotional Patterns Through Music and Health Informatics
How music listening habits and personal health informatics reveal deeper insights into mood regulation and stress management.
Lifestyle + Music
3-month Journey
Data-driven exploration of how music listening habits
intersect with daily mood, life events, and daily routines.
Methods & Tools
Diary Study
Thematic analysis of 3-months of Nightly Journals.
mood sentiments
life events
HealthKit Data
Bedtime
Sleep Time
Waking Hour
Spotify API
Inference Mood via Music Listening ‘Valence’
Tools & Data
3-month Stream History
Python
Pandas + numPy
JSON
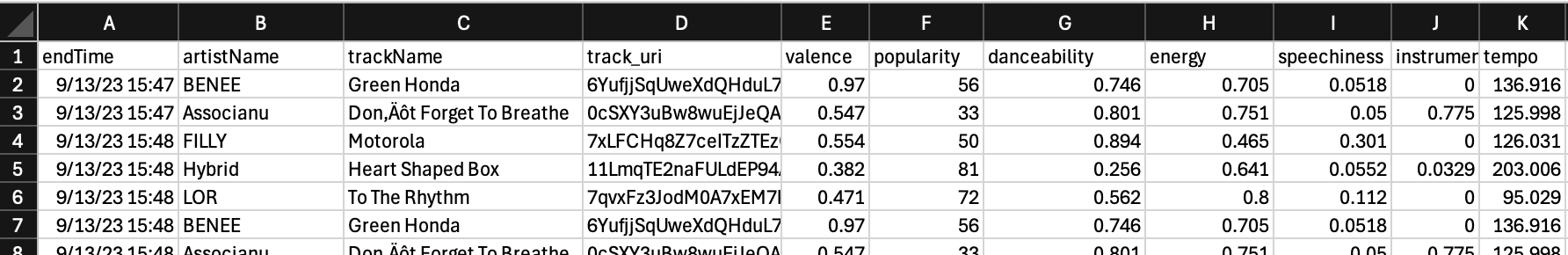
Utilized python, pandas to crosslink Spotify stream history JSON data with Spotify API Song features (mood ‘valence’) to map out longitudinal personal mood.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """Spotify Data # Spotify Music History x Spotify API 'Audio Features' """ import pandas as pd import numpy as np import requests """## Creating Streaming/Library Dataframe""" # Read Spotify StreamingHistory File df_stream1 = pd.read_json('StreamingHistory5.json') # Merge streaming dataframes df_stream = pd.concat([df_stream0, df_stream1]) # Remove White Noise/Background Music df_stream = df_stream[df_stream['artistName'] != 'Crafting Audio'] df_stream = df_stream[df_stream['artistName'] != 'Prompt Unlax'] df_stream = df_stream.reset_index(drop=True) # create a 'UniqueID' for each song by combining the fields 'artistName' and 'trackName' df_stream['UniqueID'] = df_stream['artistName'] + ":" + df_stream['trackName'] df_stream.head() import pandas as pd import json # Load JSON data from file with open('YourLibrary.json') as file: data = json.load(file) # Normalize the JSON data df_library = pd.json_normalize(data, record_path='tracks') # Adding the UniqueID column df_library['UniqueID'] = df_library['artist'] + ":" + df_library['track'] # Extracting track URI df_library['track_uri'] = df_library['uri'].str.split(':').str[2] # Display the first few rows df_library.head() # create final dict as a copy df_stream df_plays = df_stream.copy() # add column checking if streamed song is in library # not used in this project but could be helpful for cool visualizations df_plays['In Library'] = np.where(df_plays['UniqueID'].isin(df_library['UniqueID'].tolist()),1,0) # left join with df_library on UniqueID to bring in album and track_uri df_plays = pd.merge(df_plays, df_library[['album','UniqueID','track_uri']],how='left',on=['UniqueID']) df_plays.head() """## Creating Genre Dataframe""" # save your IDs from new project in Spotify Developer Dashboard CLIENT_ID = '2e592532bfcf40639103b4de477a5ffe' CLIENT_SECRET = '23ff111082cb4aad80eb609ff56fb63a' # generate access token # authentication URL AUTH_URL = 'https://accounts.spotify.com/api/token' # POST auth_response = requests.post(AUTH_URL, { 'grant_type': 'client_credentials', 'client_id': CLIENT_ID, 'client_secret': CLIENT_SECRET, }) # convert the response to JSON auth_response_data = auth_response.json() # save the access token access_token = auth_response_data['access_token'] # used for authenticating all API calls headers = {'Authorization': 'Bearer {token}'.format(token=access_token)} # base URL of all Spotify API endpoints BASE_URL = 'https://api.spotify.com/v1/' import pandas as pd import requests # Load the old features from the CSV file old_features_df = pd.read_csv('old_features.csv') # Assuming df_plays is your DataFrame containing the streaming history # Filter out tracks without a track URI in df_plays missing_uri_tracks = df_plays[df_plays['track_uri'].isna()] # Initialize an empty dictionary to store audio features feature_dict = {} # Total number of tracks to process total_tracks = len(missing_uri_tracks) # Counter for processed tracks processed_tracks = 0 # Loop through each row in the DataFrame of tracks missing URIs for index, row in missing_uri_tracks.iterrows(): # Increment the processed tracks counter processed_tracks += 1 # Extract track_uri from the DataFrame track_uri = row['track_uri'] track_found = False # Check if the track features are already in old_features_df if track_uri in old_features_df['track_uri'].values: track_features = old_features_df[old_features_df['track_uri'] == track_uri].iloc[0] feature_dict[track_uri] = track_features.to_dict() track_found = True print(f"Track {track_uri} features loaded from old_features.csv. Progress: {processed_tracks}/{total_tracks}") # If track is not found in old_features.csv, proceed with API call if not track_found: search_url = BASE_URL + 'search' search_params = { 'q': row['trackName'], # Assuming 'trackName' is a column in df_plays 'type': 'track', 'limit': 1 } search_resp = requests.get(search_url, headers=headers, params=search_params) if search_resp.status_code == 200: search_data = search_resp.json() tracks = search_data['tracks']['items'] if tracks: track_uri = tracks[0]['uri'].split(':')[2] df_plays.at[index, 'track_uri'] = track_uri # [Rest of the code for fetching and processing audio features...] print(f"Audio features successfully added for track {track_uri}. Progress: {processed_tracks}/{total_tracks}") else: print(f"No track found for {row['trackName']}. Progress: {processed_tracks}/{total_tracks}") else: print(f"Error searching for {row['trackName']}: {search_resp.status_code}. Progress: {processed_tracks}/{total_tracks}") # Convert feature_dict to DataFrame df_features = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(feature_dict, orient='index') df_features.insert(0, 'track_uri', df_features.index) df_features.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True) df_features.to_csv('simple_features.csv') # Assuming 'df_plays' is the DataFrame you want to output # You may have modified or added to it in your previous code df_plays.to_csv('combined_data.csv', index=False)
Dataframes
Merged 2818 Songs + Spotify Audio Features (‘valence, popularity, etc’)
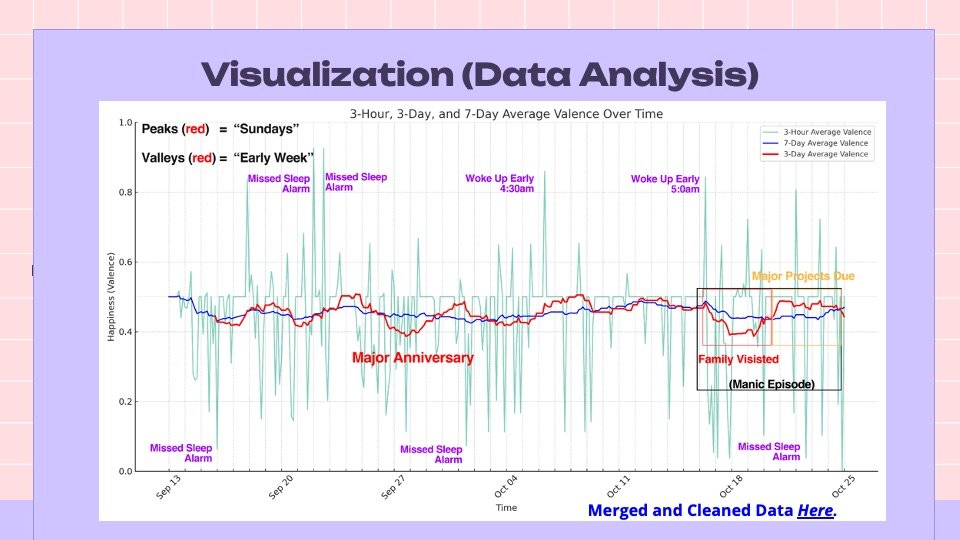
Insights
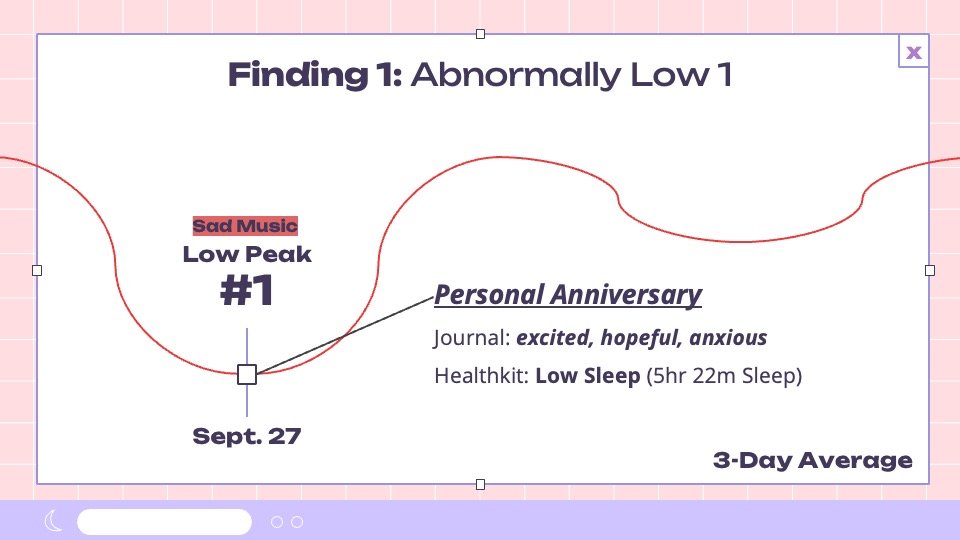
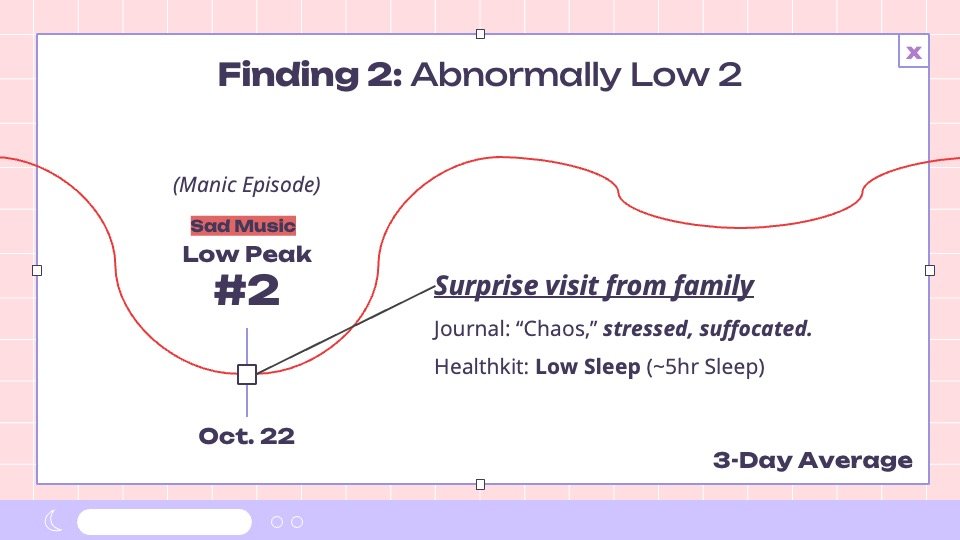
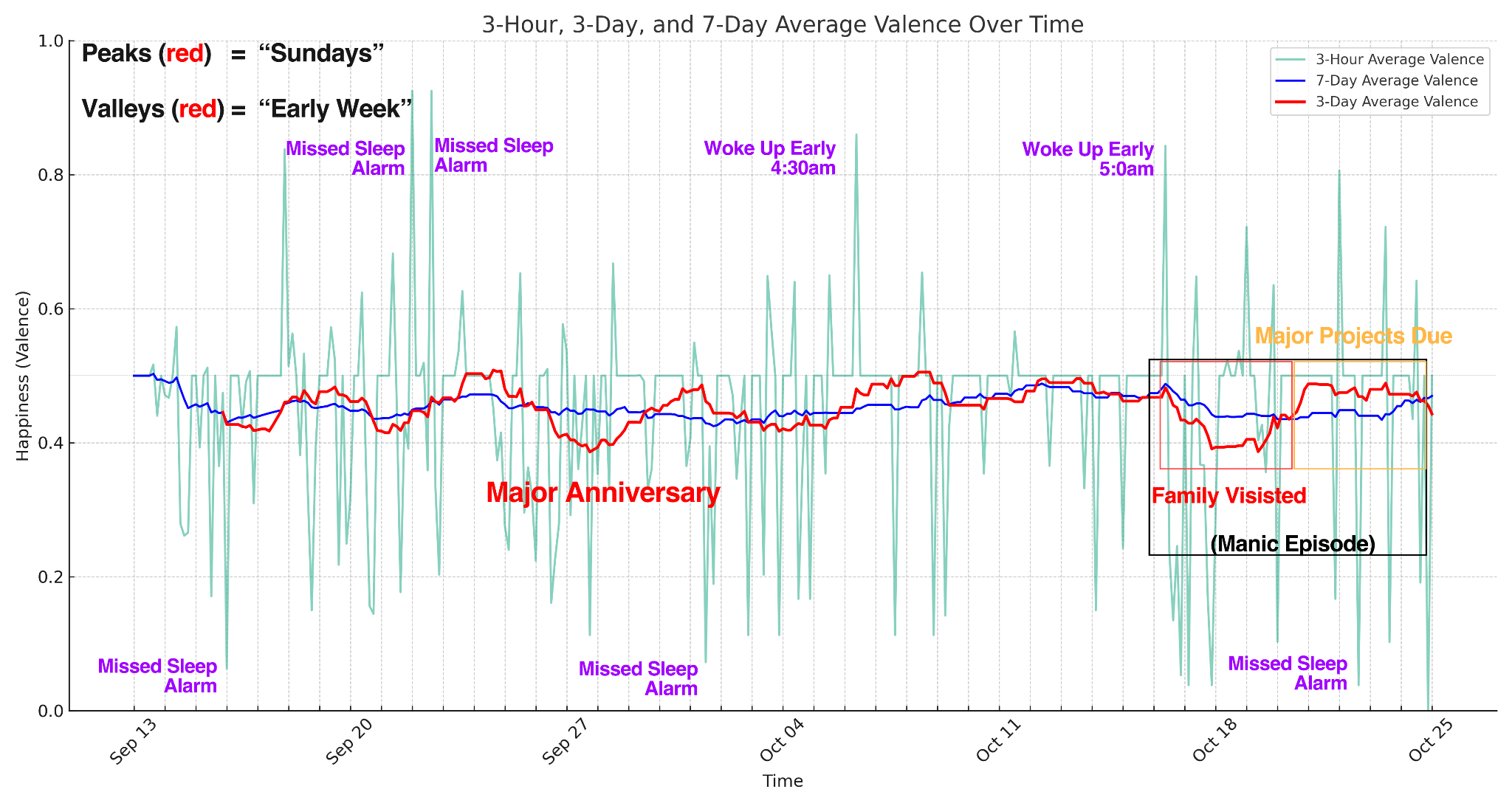
Sad Music
Sadder music appeared during chaotic life events and reflective moments.
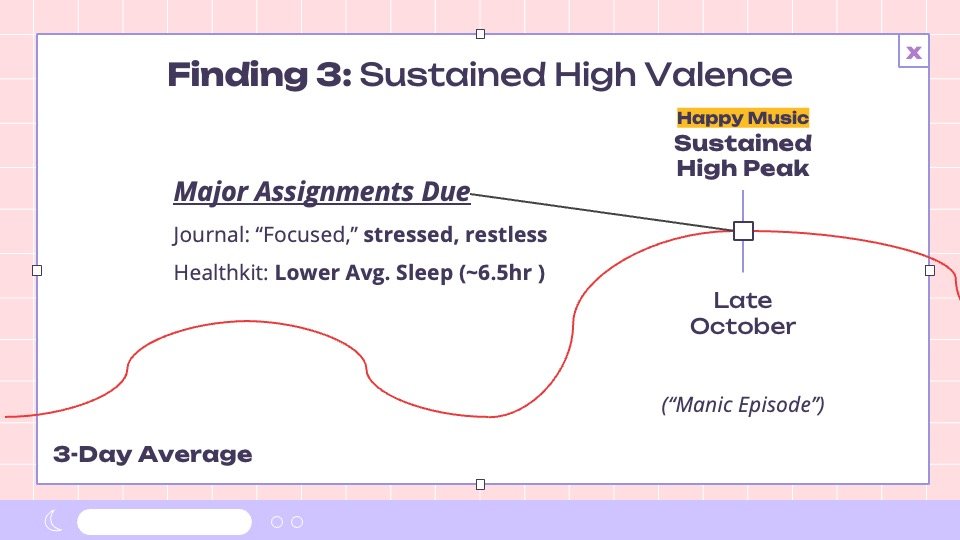
Happy Music
Happier music was more frequent during weekends and high-focus stress periods.
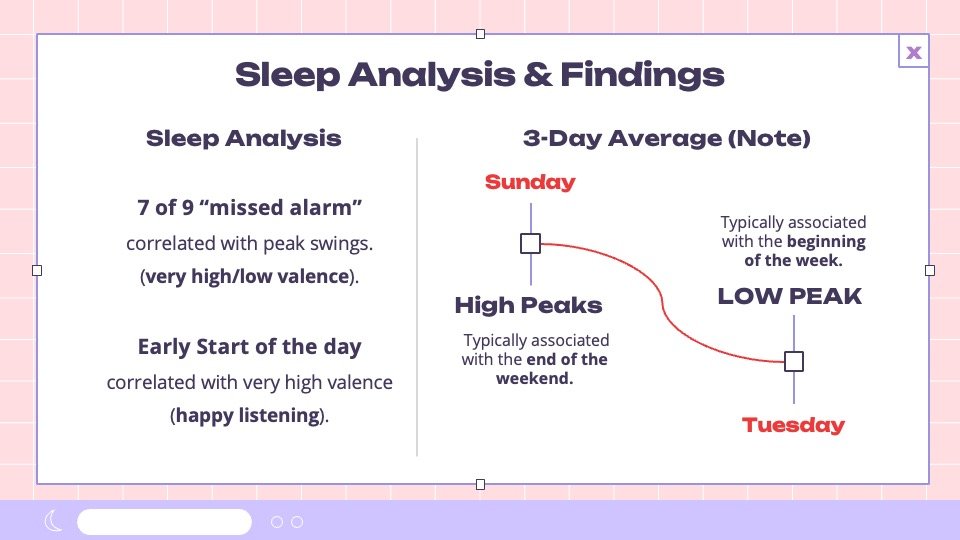
Sleep Correlation
Early mornings showed a clear spike in listening to happy, energizing music.